What Is Human Evolution?
- Laurie L.

- Apr 10, 2018
- 2 min read
Updated: Jun 24, 2022
Anthropology
The first thing any Anthropologist will tell you about human evolution is that humans came from Africa and have been around for about 315,000 years (315Ka). Scientists have traced DNA of our most recent common ancestors to Africa through the MITOCHONDRIAL EVE and the Y CHROMOSOME ADAM. For information about DNA, click this LINK. Our ancestry can also be traced by examining human-like fossils for signs of bipedalism. For more information about how bipedalism developed, click this LINK.

The processes of evolution, found HERE, don't have a beginning or end goal in mind. Human traits developed because it benefited our species at the time. We can separate evolution and religion on this idea with a simple example. If a painter paints a bridge, the paint didn't decide to become a bridge. In this case, the goal of science isn't to define and understand the painter. The role of science is to study the painting. Evolution didn't plan for humans to exist. Scientifically, we can't assume there's any meaning behind our existence, physically, except that our physical forms allowed us and even helped us to survive and reproduce to the present.
Evolutionary Ideas
LAMARCKIAN EVOLUTION was used to fight against the idea of natural selection. The idea was that a person worked out and exercised a lot, they would have a musclebound baby. Darwinian evolution, which holds true today, is species experiencing constant branching and divergence in nature to fill available niches (living spaces). Think back to my previous post about microevolution and macroevolution (for more information, click HERE).

The picture above is from the journal of Charles Darwin depicting his first insight on evolution.
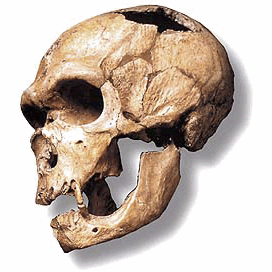
The traits of human ancestors are easily identified by the trained eye. The structures include brain size, precision grip, and bipedalism. Anthropologists can tell just by one tooth fossil whether something is a human or an ancestor. For more information about bipedalism, click HERE.
There's many hypotheses about how humans came to be and what caused bipedalism to evolve. There's also debate about whether Homo neanderthalensis, another species almost just like us, should be considered human because almost everyone has Neanderthal DNA in them today.
The scientific method, evolutionary processes, dating methods, taxonomy, ecology, and every biological study are not just built on the previous works, but also support it through evidence. If the research didn't support evolution, then scientists would never agree about the fundamentals of evolution and how the world works.
Sources:
Theories of Human Evolution: A Century of Debate, 1844-1944 by Peter J. Bowler
Laboratory Manual and Workbook for Biological Anthropology: Engaging with Human Evolution by K. Elizabeth Soluri and Sabrina C. Agarwal
Lecture Notes: Dr. Kurtis Dean and Dr. James Loch, Evolution, Fall 2018
Lectures Notes: Dr. Hannah Marsh, Human Prehistory, Fall 2014; Human Variation, Spring 2016; Human Evolution, Fall 2016










Comments